
Importantly, we were able to demonstrate that a reasonable level of competence could be achieved after a very brief training period. The results of our study suggest that S aureus growing in BacT/ALERT blood culture bottles can be identified by direct Gram stain characteristics with a high degree of accuracy. The ability to identify S aureus bacteraemia rapidly and accurately has direct clinical relevance for prompting the initiation of antibiotic treatment or a change to a more appropriate antibiotic regimen.
GRAM POSITIVE COCCI CLUSTERS SERIES
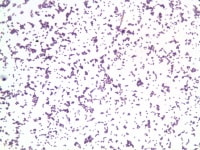
The microbiologist, who had not previously used the diagnostic criteria first hand, then examined the same series of Gram stains in a blinded fashion. To assess how readily this technique can be taught, the same technologist trained a clinical microbiologist in the use of these criteria by showing typical examples of the key distinguishing characteristics. At the time the slides were examined, the technologist knew whether the Gram stains were from aerobic or anaerobic blood culture bottles, and all Gram stains were assessed before the culture results were known. Laboratories using the BacT/ALERT blood culture system should become familiar with these criteria for the rapid identification of S aureus bacteraemiaĭirect Gram stains of blood culture broth made after the bottles signalled positive were examined by an experienced technologist, who classified the organism as S aureus or not based on the criteria listed in table 1. This method was readily taught to a clinical microbiologist who had not previously used the method The overall sensitivity was 89% and specificity was 98% We have developed a series of criteria based on direct Gram stain characteristics that enabled an experienced microscopist to distinguish S aureus from other staphylococci isolated from BacT/ALERT blood culture bottles The rapid identification of Staphylococcus aureus from positive blood cultures provides important clinical and therapeutic information The purpose of our study was to evaluate these criteria in a blinded prospective fashion. The main characteristics are the size of the bacterial cells, the number of cells in a typical cluster, and knowledge about whether the Gram stain was made from an anaerobic or aerobic blood culture bottle (table 1 fig 1). Over the past decade, technologists in our laboratory have noted that certain morphological characteristics can help distinguish S aureus from coagulase negative staphylococci in direct Gram stains from BacT/ALERT blood culture bottles (BioMérieux, Durham, North Carolina, USA). “The main characteristics are the size of the bacterial cells, the number of cells in a typical cluster, and knowledge about whether the Gram stain was made from an anaerobic or aerobic blood culture bottle” This distinction is important given the differences in virulence, and the relatively high frequency that coagulase negative staphylococci are isolated as contaminants. The appearance of Gram positive cocci in clusters on direct Gram stain is suggestive of staphylococcus species, but differentiation of Staphylococcus aureus from coagulase negative staphylococci can usually only be made 18–24 hours later, once the organism has been cultured on solid media. Once a positive blood culture is detected, presumptive identification of the organism relies on direct Gram stain of the inoculated blood culture broth. The use of continuously monitored blood culture systems has reduced the time taken to detect positive blood cultures.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
